Blog
What is Digital Marketing? Your Essential Guide to the Digital World
Unlock Your Brand’s Potential: The Ultimate Guide to Dominating the Digital Landscape
Table Of Content
Toggle
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing refers to the use of digital channels, platforms, and technologies to promote products, services, or brands to a target audience. Unlike traditional marketing, which relies on physical mediums like print ads or billboards, digital marketing leverages the internet, social media, search engines, email, and other digital tools to reach potential customers.
Digital marketing is the practice of promoting products, services, or brands through digital channels such as websites, social media, search engines, email, and mobile apps. It involves a range of strategies and tactics aimed at reaching and engaging a target audience online. Unlike traditional marketing, digital marketing allows for highly targeted and measurable campaigns, enabling businesses to reach their desired audience with precision and track the effectiveness of their efforts in real-time.
Digital Marketing: Key Points
- Definition: Promotion of products, services, or brands using online channels and technologies.
- Core Channels: SEO, content marketing, social media, email marketing, PPC advertising, affiliate marketing, influencer marketing, and mobile marketing.
- Objectives: Increase brand awareness, generate leads, drive sales, and engage customers.
- Targeting: Personalized and data-driven campaigns based on audience behavior and demographics.
- Measurement: Use of analytics to track performance and optimize campaigns.
- Global Reach: Accessible 24/7, scalable, and cost-effective compared to traditional marketing.
- Content Types: Blogs, videos, infographics, podcasts, e-books, and more.
- Evolving: Rapidly adapts to new technologies and trends like AI and video content.
- Interactivity: Enables two-way communication and real-time feedback.
- Integration: Works alongside traditional marketing for a cohesive strategy.
Importance of Digital Marketing
Wider Reach:
Digital marketing allows businesses to reach a global audience, breaking geographical barriers and expanding their market reach.
Cost-Effective:
Compared to traditional marketing methods, digital marketing is often more affordable, providing a high return on investment (ROI), especially for small businesses and startups.
Targeted Audience:
With tools like social media advertising and search engine marketing, businesses can target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors, ensuring that their marketing efforts reach the right people.
Measurable Results:
Digital marketing provides real-time data and analytics, allowing businesses to track the performance of their campaigns, understand customer behavior, and make informed decisions to optimize their strategies.
Enhanced Engagement:
Digital platforms enable direct interaction with customers, fostering stronger relationships through personalized communication, social media engagement, and responsive customer service.
Flexibility and Adaptability:
Digital marketing campaigns can be quickly adjusted based on performance data, enabling businesses to respond to market changes and consumer trends with agility.
Brand Building:
Consistent online presence and effective content marketing help in building brand awareness, trust, and loyalty among consumers.

How Digital Marketing Works?
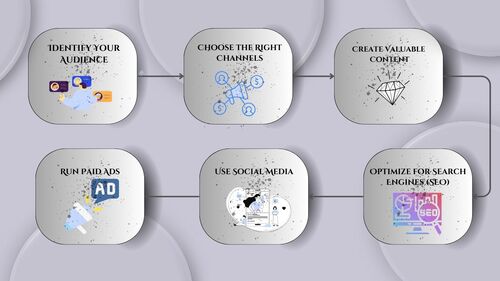
Digital marketing works by using the internet and digital platforms to promote products, services, or brands to potential customers. Here’s a simple explanation:
Identify Your Audience:
The first step is to understand who your target customers are—what they like, where they spend their time online, and what problems they need solving.
Choose the Right Channels:
Based on where your audience is, you select digital channels to reach them. These can include social media, search engines, websites, email, and more.
Create Valuable Content:
You develop content that addresses your audience’s needs and interests. This could be blog posts, videos, social media updates, emails, or ads. The goal is to attract, inform, and engage your audience.
Optimize for Search Engines (SEO):
By optimizing your content with relevant keywords, you ensure it shows up in search engine results when people look for information related to your business.
Use Social Media:
You share your content on social media platforms to increase visibility and engage with your audience. Social media is also great for running targeted ads to reach specific groups.
Run Paid Ads:
You can use Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising on platforms like Google ads or Facebook ads to drive traffic to your website or landing pages. You only pay when someone clicks on your ad.
Engage with Email Marketing:
Send personalized emails to your subscribers to nurture relationships, promote products, and encourage repeat business.
Analyze and Improve:
Use analytics tools to track how well your digital marketing efforts are working. Look at what’s successful and where you can improve. Adjust your strategies based on these insights.
Types of Digital Marketing Channels
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Content Marketing:
Content marketing is a strategic approach to digital marketing that focuses on creating, distributing, and promoting valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a specific target audience. The ultimate goal is to drive profitable customer actions, such as making a purchase, subscribing to a service, or increasing brand loyalty.
Social Media Marketing:
Social Media Marketing (SMM) is the use of social media platforms to promote a product, service, or brand. It involves creating and sharing content, engaging with followers, and running paid advertising campaigns to achieve marketing and branding goals. The primary aim of social media marketing is to connect with your audience, build your brand, increase sales, and drive website traffic.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising:
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising is a digital marketing model where advertisers pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. It’s essentially a way of buying visits to your site, rather than attempting to “earn” those visits organically. PPC ads can appear on search engines, social media platforms, and other websites, allowing businesses to target specific audiences and achieve a variety of marketing goals.
Email Marketing:
Email marketing is a form of direct digital marketing that involves sending targeted emails to a group of recipients, typically customers or prospects, with the goal of promoting products, services, or building customer relationships. It’s a powerful tool for businesses to connect with their audience, nurture leads, and drive conversions.
Affiliate Marketing:
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based marketing strategy where businesses reward affiliates (partners) for driving traffic, leads, or sales to their website through the affiliate’s marketing efforts. Affiliates earn a commission for each action (such as a sale or a click) that results from their promotional activities. This model is popular because it allows businesses to expand their reach and sales without upfront marketing costs.
Influencer Marketing:
Influencer marketing is a strategy where brands collaborate with influential people—typically on social media—to promote products, services, or brand messages. These influencers have established credibility, a loyal following, and the ability to sway the opinions and purchasing decisions of their audience. Influencer marketing leverages this trust to reach potential customers in a more authentic and relatable way than traditional advertising.
Display Advertising:
Display advertising refers to the practice of using visually appealing ads—such as banners, images, videos, or interactive elements—to promote products, services, or brand messages on websites, apps, or social media platforms. These ads are typically placed on third-party websites or platforms, allowing businesses to reach a wide audience beyond their own website.
Mobile Marketing:
Mobile marketing refers to strategies and tactics that engage and reach customers through their mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Given the widespread use of mobile devices, mobile marketing has become a crucial component of digital marketing, enabling businesses to connect with consumers on the go.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Digital Marketing
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in digital marketing are measurable metrics that help businesses assess the effectiveness of their marketing strategies. These indicators are crucial for understanding how well a campaign is performing, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring that marketing efforts align with business goals. Here are some of the most important KPIs in digital marketing:
1. Website Traffic:
- Total Visits: The total number of visits to your website. This helps gauge overall interest in your brand.
- Traffic Sources: Where your website traffic is coming from (e.g., organic search, social media, direct, referrals). This helps identify which channels are most effective.
- New vs. Returning Visitors: The ratio of first-time visitors to repeat visitors, indicating how well your content is engaging users over time.
2. Conversion Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (e.g., making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter).
- Importance: High conversion rates indicate that your marketing efforts are successfully driving users to take the intended action.
3. Bounce Rate:
- Definition: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page.
- Importance: A high bounce rate may indicate that your website content or user experience isn’t engaging or relevant to visitors.
4. Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Definition: The percentage of people who click on a link or ad compared to the total number of people who see it.
- Importance: High CTRs suggest that your ads or email campaigns are compelling and resonate with your audience.
5. Cost Per Acquisition (CPA):
- Definition: The average cost to acquire a new customer through a particular campaign.
- Importance: Keeping CPA low while maintaining or increasing conversions is a key goal in digital marketing to ensure profitability.
6. Return on Investment (ROI):
- Definition: The revenue generated from a campaign relative to the cost of running it.
- Importance: ROI helps measure the overall effectiveness and profitability of your marketing efforts.
7. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV or LTV):
- Definition: The total revenue expected from a customer over the course of their relationship with your brand.
- Importance: A high CLV indicates that your business is effectively retaining customers and maximizing their value.
8. Social Media Engagement:
- Likes, Shares, Comments: The level of interaction your social media content receives.
- Followers Growth: The rate at which your social media audience is growing.
- Post Reach: The number of people who see your social media content.
- Importance: These metrics indicate how well your content is resonating with your audience and expanding your brand’s visibility.
9. Email Marketing Metrics:
- Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who open your email. A high open rate indicates effective subject lines and targeted content.
- Click-Through Rate (Email): The percentage of recipients who click on links within your email, showing the effectiveness of your email content.
- Unsubscribe Rate: The percentage of recipients who opt-out of your email list. A high rate could signal that your content is not meeting subscribers’ expectations.
10. Search Engine Rankings:
- Keyword Rankings: The position of your website in search engine results for specific keywords.
- Organic Search Traffic: The number of visitors coming to your site through unpaid search results.
- Importance: High rankings and increased organic traffic suggest that your SEO efforts are successful.
11. Cost Per Click (CPC):
- Definition: The amount you pay for each click on your paid ads.
- Importance: Lowering CPC while maintaining high CTR can improve the cost-efficiency of your paid campaigns.
12. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC):
- Definition: The total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses.
- Importance: Lowering CAC is essential for increasing the profitability of your customer acquisition strategies.
13. Engagement Rate:
- Definition: The ratio of interactions (likes, comments, shares) to the total reach of a piece of content.
- Importance: A high engagement rate indicates that your content is effectively engaging your audience.
14. Average Session Duration:
- Definition: The average amount of time a visitor spends on your website during a single session.
- Importance: Longer session durations suggest that visitors find your content valuable and engaging.
15. Lead Generation:
- Number of Leads: The total number of potential customers who have shown interest in your products or services.
- Lead Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into paying customers.
- Importance: Effective lead generation and conversion indicate a successful funnel from interest to purchase.
Why Website is Important in Digital Marketing
1. Central Hub for Online Presence:
- Brand Identity: Your website serves as the primary platform where customers can learn about your brand, products, and services. It establishes your brand’s identity and credibility.
- Content Repository: It’s where you can publish and manage content, including blog posts, videos, and case studies, that helps engage and educate your audience.
2. Increases Visibility and Reach:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): A well-optimized website improves your visibility in search engine results, driving organic traffic to your site.
- Global Reach: Unlike physical locations, a website can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection, expanding your reach beyond geographical boundaries.
3. Lead Generation and Conversion:
- Lead Capture Forms: Websites can include forms for capturing leads, such as contact forms, sign-ups for newsletters, or requests for quotes.
- Call-to-Action (CTA) Buttons: Effective CTAs guide visitors toward taking desired actions, such as making a purchase, scheduling a consultation, or downloading a resource.
4. Analytics and Insights:
- Tracking User Behavior: Tools like Google Analytics provide data on how visitors interact with your site, including page views, time spent on pages, and bounce rates.
- Performance Measurement: You can track the effectiveness of your digital marketing campaigns by monitoring metrics such as conversion rates and traffic sources.
5. Customer Engagement and Support:
- Interactive Features: Websites can include features like chatbots, forums, and contact forms to facilitate customer engagement and support.
- Content and Resources: Providing valuable content, such as FAQs, guides, and tutorials, helps address customer questions and build trust.
6. Credibility and Trust:
- Professional Image: A well-designed and functional website enhances your brand’s professional image and credibility.
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Showcasing positive reviews and testimonials on your website can build trust and influence potential customers.
7. Support for Other Marketing Channels:
- Social Media Integration: Your website can integrate with social media channels, driving traffic and engagement from platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Email Marketing: Email campaigns can drive traffic to your website, where recipients can take further actions or explore additional content.
8. E-Commerce and Sales:
- Online Store: For businesses selling products, a website acts as an online store, allowing customers to browse, select, and purchase items.
- Order Management: You can manage orders, inventory, and customer data directly from your website, streamlining your sales process.
9. Brand Control and Ownership:
- Complete Control: Unlike social media platforms where you are subject to their rules and algorithms, your website gives you full control over your content, design, and user experience.
- Brand Messaging: You can tailor your messaging and content to align with your brand’s values and goals without restrictions.
10. Data Collection and Personalization:
- User Data: Collecting data from website visitors allows you to understand their preferences and behaviors, enabling personalized marketing efforts.
- Targeted Campaigns: You can use the insights gained to create targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with your audience.
11. Competitive Advantage:
- Differentiation: A unique and user-friendly website can differentiate your business from competitors, showcasing what makes you stand out.
- Market Positioning: Your website can reflect your brand’s positioning in the market, helping to attract your target audience and establish your business as a leader.
Pros and Cons of Digital Marketing: Unlocking Success While Navigating Challenges
Merits of Digital Marketing
Global Reach:
Digital marketing allows businesses to reach a global audience, breaking geographical boundaries and opening new markets across the world. A small business can attract customers from multiple countries, expanding its footprint significantly.
Cost-Effective:
Compared to traditional marketing methods (like TV or print ads), digital marketing is far more affordable. Pay-per-click (PPC) ads, social media campaigns, and email marketing can be done with modest budgets, making it accessible for small businesses.
Targeted Audience:
Digital marketing tools offer precise audience targeting based on demographics, behavior, interests, and location. This ensures that your marketing efforts are directed toward those most likely to convert, increasing efficiency and ROI.
Measurable Results:
Tools like Google Analytics, social media insights, and email marketing software allow businesses to track real-time data and performance metrics. You can see which campaigns are working, what needs improvement, and adjust accordingly.
Personalization:
Digital marketing enables personalized customer experiences. Through data collection and analytics, businesses can tailor content, product recommendations, and offers to individual users, making them feel valued and increasing engagement.
Interactivity and Engagement:
Through platforms like social media, businesses can interact directly with their audience, respond to inquiries, and build relationships. This fosters brand loyalty and community engagement.
Improved Conversion Rates:
By targeting specific audiences and offering engaging content, digital marketing typically results in higher conversion rates compared to traditional methods. Well-designed landing pages, clear calls to action, and optimized ads increase the likelihood of converting visitors into customers.
Scalability:
Digital marketing campaigns can easily be scaled up or down based on budget and performance. Whether a business has $100 or $10,000 to spend, they can create effective campaigns that meet their goals.
Flexibility in Strategy:
With the wide variety of formats available—such as search engine marketing (SEM), social media, email, content, and video—businesses can quickly pivot and experiment with different strategies to find what works best for their audience.
Brand Development:
Through consistent digital marketing efforts (blogging, social media, SEO), businesses can develop a recognizable and authoritative brand image. Regular content creation helps to establish trust and credibility in the marketplace.
Demerits of Digital Marketing
High Competition:
The accessibility of digital marketing means that virtually every business is online, resulting in intense competition. Standing out in a crowded marketplace can be difficult, especially for smaller businesses with limited budgets.
Privacy and Security Issues:
Collecting user data for targeted marketing raises concerns about privacy. Businesses must ensure they comply with data protection laws (like GDPR) and have secure systems in place to prevent breaches, or they risk losing customer trust.
Time-Consuming:
Effective digital marketing requires constant attention, frequent content updates, and ongoing optimization. This can be time-consuming, especially for small businesses with limited resources or marketing teams.
Overwhelming Technology and Tools:
Digital marketing involves various tools and platforms for content creation, analytics, social media management, and SEO. For those unfamiliar with technology, this can be overwhelming and requires a learning curve.
Dependence on the Internet:
Digital marketing is heavily reliant on internet access. If customers have poor connectivity or are located in areas with limited online access, your campaigns may not reach them effectively.
Constant Algorithm Changes:
Platforms like Google and Facebook frequently update their algorithms, which can significantly impact visibility and ranking. Businesses need to stay up-to-date with these changes and adjust strategies accordingly, which can be challenging.
Risk of Negative Feedback:
Digital marketing opens businesses to direct feedback, both positive and negative. Negative reviews or public complaints on social media can damage a brand’s reputation if not managed effectively.
Ad Fatigue:
Users exposed to a high volume of ads may become desensitized or even annoyed by constant marketing efforts. This can lead to a decrease in engagement or users actively avoiding ads, making campaigns less effective.
Requires Expertise:
Digital marketing involves a range of specialized skills, including SEO, content creation, data analysis, and social media management. Without proper expertise, businesses may struggle to develop and implement successful campaigns.
Ad Blocking:
Many users install ad blockers, which prevent ads from displaying. This reduces the effectiveness of paid advertising campaigns, especially display and video ads, leading to lost opportunities for engagement.
